Home
AirLink uses financed phones as relay-extensions of the internet in remote areas, to extend productive asset data coverage in even the most rural communities. By introducing open-standards communications, AirLink allows customers’ phones and PAYGo assets to communicate with each other by using widely available, standard low-energy Bluetooth connectivity.
This is technical documentation for AirLink. If you are looking for an overview of the AirLink project, see this:
Use cases¶
For all potential use cases, EnAccess hosts the IoT server for free so that you can try your idea quickly and cost effectively! 🏁 Quick-start guide
How to use AirLink in some common uses:
A Device Manufacturer developing devices to be used in remote-region IoT data collection or PAYGO-financed use¶
 An NGO wanting to define a adaptable hardware/software standard for data collection in your projects or grantees¶
An NGO wanting to define a adaptable hardware/software standard for data collection in your projects or grantees¶
A Fintech/PAYGO entrepreneur focused on innovative software, needing a standard hardware spec to share with a device manufacturer¶
AirLink components¶
AirLink devices (Nordic nRF firmware)¶
AirLink App (Flutter app)¶
AirLink Server (Thingsboard server configuration)¶
Key ideas built into AirLink¶
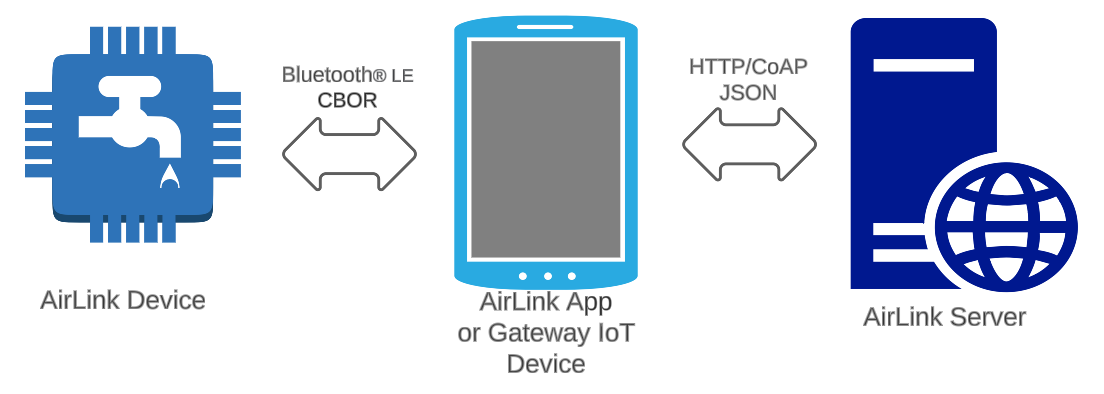
BLE-GSM Data transfer¶
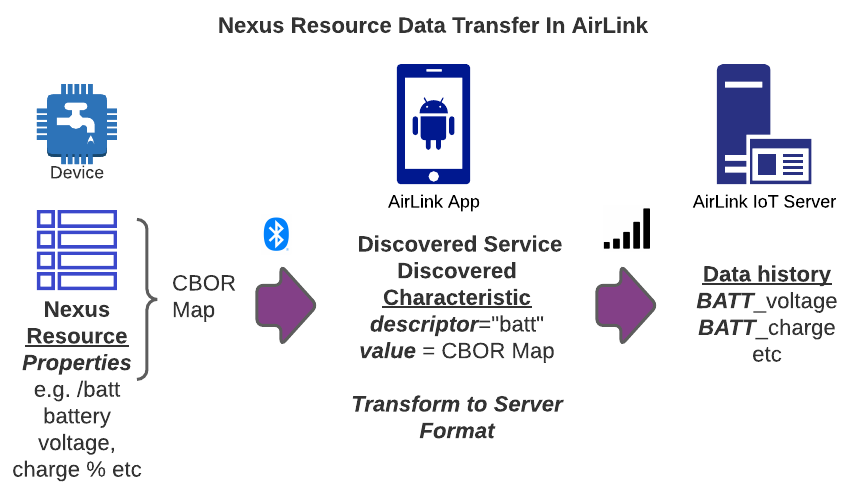
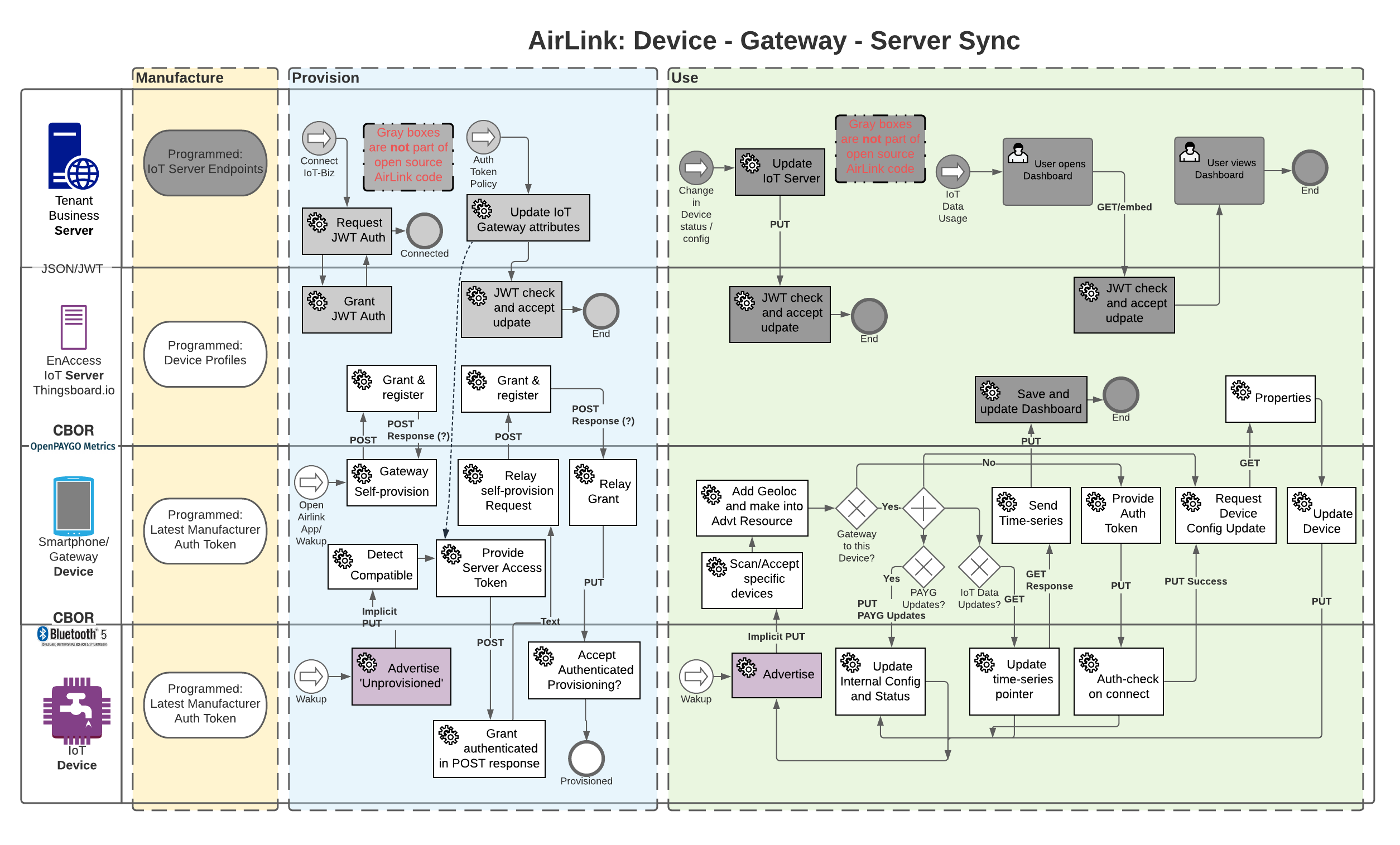
IoT Device Lifecycle¶
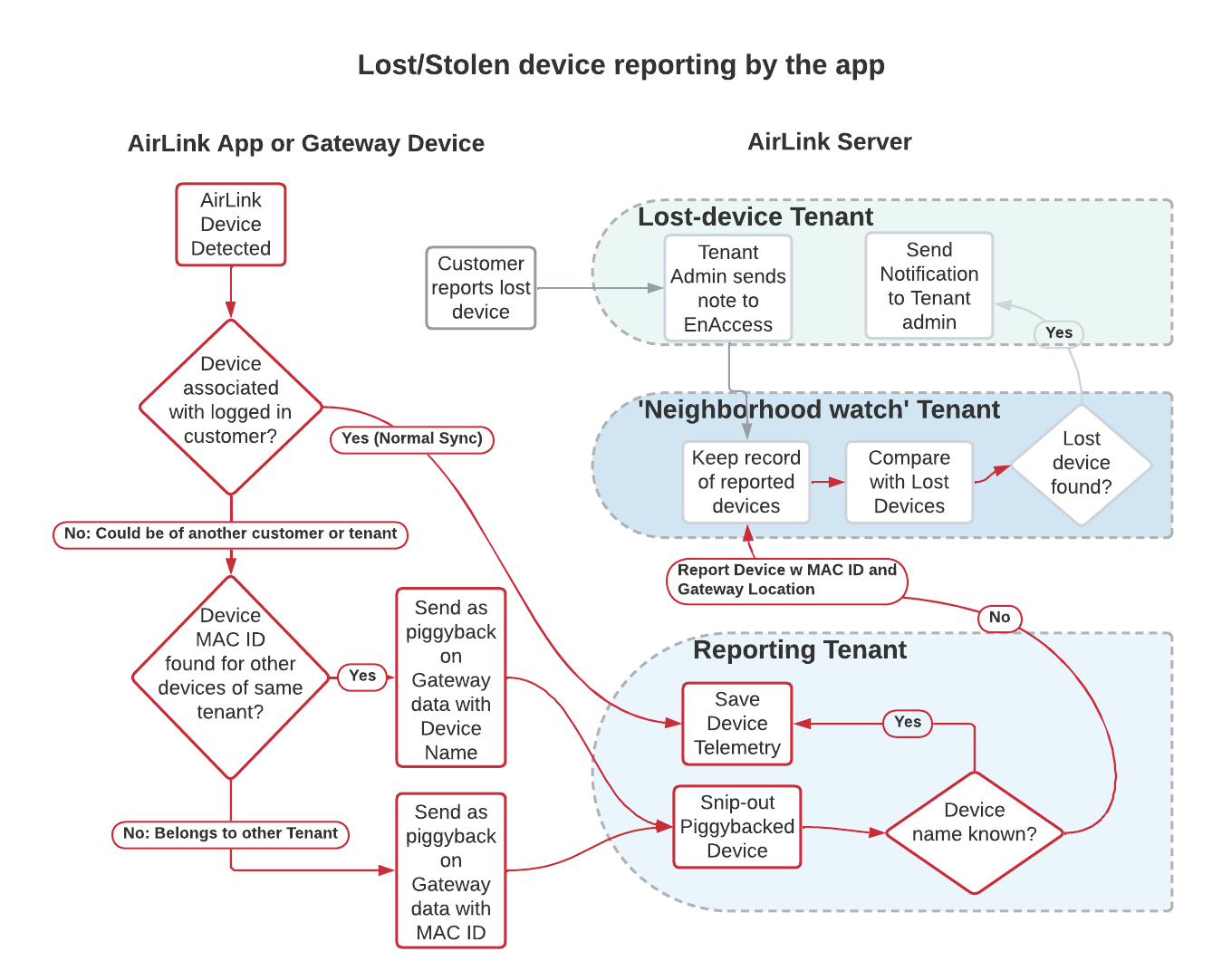
App-driven, Crowdsourced locatability¶
PAYGO control¶
Related resources¶
- CBOR: Memory-efficient JSON-like data format
-
OCF: Data structure standard to represent IoT devices
-
Nexus Channel: Angaza's Inter-operability initiative
- OpenPAYGO Link: Wired inter-operability from Solaris/EnAccess
- OpenPAYGO Metrics: GSM inter-operability from Solaris
- OpenPAYGO Token: Open Source PAYGO token reference design from Solaris/EnAccess

AirLink was developed by Simusolar Inc with support from EnAccess.

